Enceladus, Life for good?
Enceladus, Life for good?
An article by Igor Otto (study being written based on notes and research since 2014)
Various artist's views of submarine extraterrestrial phylums.
Meteorite bombardment, which is very ancient throughout the solar system, is also an abundant source of complementary carbon in any medium (eg Antarctic Micrometeorites on Earth) and thus with the carbon intake of these, the theory of the panspermia is not far ...
It is possible that Enceladus was subjected like a Moon to a period of intense bombardment 3.5 to 4 billion years ago without counting the effects of a pounding of the surface even more intense during the Large late bombardment (theoretical period in the history of the solar system approximately 4.1 to 3.9 billion years ago, during which meteoric or cometary impacts would have occurred on the terrestrial planets in a very important way).
Meteorite bombardment is also a source of amino acids, and thus more than 70 amino acids, including 8 of the 20 proteins that are known to be of extra terrestrial origin on Earth since found in many meteorites, for example: Meteorite of Murchison.
In deep space, 141 molecules have been discovered including methane: CH₄, ethyl alcohol: C₂H₅OH, formaldehyde (CH2O) or acetic acid: CH₃COOH as in the Eagle Nebula (M16) and amino acids as on the comet "Tchouri", 67P / Churyumov-Gerasimenko, (ESA, 2004-2016) such as glycine, measured during the CNES Rosetta mission [and also previously detected by the American Stardust probe (NASA, 1999- 2011, and the first to bring particles of a comet back to Earth) in the plume of the Wild 2 comet, as well as phosphorus, an essential component of DNA and many organic compounds have been detected there. Being the sixth comet visited by missions and on which organic compounds are discovered, some mandatory and necessary for life, it seems quite logical to think that the bricks of life are common in the space environment.
Each amino acid consists of an amine function (NH 2), a carboxylic acid function (COOH-) and a variable side chain (R).
Amino acids are molecules that are part of the protein composition and vital for the proper functioning of any living metabolism. These bonds are called peptides. There are about 100 amino acids, but only 22 are coded by the genome of living organisms, 4 of which are DNA. Each amino acid gives the protein specific chemical properties, and the assembly order gives it a very precise 2D and 3D function and can be folded back.
From an exobiological point of view, essential and varied ion exchanges are therefore at stake between rock and liquid water, in keeping with the existence of possible forms of life according to our knowledge. It is still unclear whether there are all the necessary components but to date, many are available and can be reunited so that life exists on Enceladus. In any case, there are many reactions of oxydo-reductions and redox in action there! This satellite is one of only four objects in the Solar System (with Jupiter's satellite, Io, Neptune's, Triton's, and of course the Earth's) on which eruptions or material ejections could be directly observed.
Enceladus revolves around Saturn (Saturn has 62 known moons, 53 of which have formal names; in addition, there is evidence of dozens to hundreds of moonlets with diameters of 40–500 meters in Saturn's rings, which are not considered to be true moons) within the outermost and most tenuous ring of all, called ring E; this ring would be fed permanently in particles by the current (or recent) "volcanic eruptions" of Enceladus that one could also go to study. Moreover, the formidable tidal forces as plasma fluxes resulting from the gravitational action of the neighboring giant Saturn form an enormous energy supply, and a geophysical argument favourable to the hypothesis of the presence of life in the form of creatures diverse and perhaps not so strange on this moon as others around some solar planets and subsequently in other stellar and exolune systems ...
It is therefore necessary also to analyse its neighbours within the ring E, namely three major internals satellites of Saturn which orbit there, in the company of the three small moons of the group of Alcyonides, namely:
Note: It may be speculative to date to use the model Ĕ but it is a tool that can be useful now and will soon be validated by the various data collected.
Since 2012, NASA has been conducting missions such as LIFE (Life Investigation For Enceladus, pdf of description of the mission) by Peter TSOU, or the Enceladus Life Finder mission that was proposed in 2015 to finance the Discovery Mission Mission, one of NASA's exploration programs.
The final design of Life Investigation For Enceladus (LIFE) in 2015 includes a sample return module inherited from the Japanese Haybusa probe (ie: Peregrine Falcon, which reached asteroid Itokawa in 2005, the capsule containing the samples is returned at a short distance from the Earth on June 13, 2010. This capsule, in the shape of a saucer, measured 40 cm in diameter and 25 cm in height for a mass of approximately 17 kg. The end facing forward during atmospheric reentry was covered by an ablative heat shield 3 cm thick to protect its contents from heat, close to 3000 ° C, generated
 by its re-entry speed, and the receptacle contained 1543 particles, the size of which was between 3 and 40 micrometers) and equipped with a multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG for Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator)
by its re-entry speed, and the receptacle contained 1543 particles, the size of which was between 3 and 40 micrometers) and equipped with a multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG for Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator)
If one of them is selected, a preparation date for the launch to 31 December 2021 may still be possible. The project is to collect water / particles ejected in space with a probe equipped with a battery of collectors and instruments of measurements of analysis in situ, in space, to verify the nature of the elements The speed of release at the surface of Enceladus is about 865 km / h, ie 0.241 km / s, which is not too much of a problem, but probing the very deep, is out of our present means, and this with a mission of study even more important because a priori, science has no direct evidence of the reality of a local life. However, as a more precise and thorough analysis of the compounds released from these hydrothermal sources is necessary, it will be necessary at all costs to bring the recovered samples back to Earth. The probe would have only to position itself at the South pole to collect water samples in space, and thanks to its built-in instruments try to measure, classify, inventory, record all particles and informations for the search for Life on Enceladus and then return to Earth so that scientists can better study direct evidence harvested ....
The raw images of the water geysers and the Enceladus flyover are here: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=4759
Compared to the Earth, micro-organisms in the hydrothermal springs of the famous Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming derive most of their energy from hydrogen, not sulfur, as was thought. Research conducted over several years led a team from the University of Colorado to Boulder to this conclusion. The researchers first studied the phylogenetic composition of microbial populations living in hot springs in Yellowstone at over 70 ° C. Molecular analyzes have shown that the majority of the biomass of these systems is composed of organisms using hydrogen oxidation to obtain energy.
Finally, computer-generated thermodynamic (energy study) models have completed a portrait of an extremophilic ecosystem based on hydrogen-related metabolic functioning despite high sulfur content.
The NASA has already announced the discovery of many types of molecules including hydrogen on Enceladus on its surface, thanks to a brief overview of the Cassini probe (launched in 2004) which was carried out at an altitude of 49 kilometers at the SOUTH pole, October 28, 2015, through plumes of water vapor and ice particles, which could be an indication of the presence of extraterrestrial life in the Solar System. It is the instrument Ion and Neutral Mass Spectrometer (INMS) embarked that analyzed the composition, this one was originally intended to study the upper layers of the atmosphere of Titan.
It should be noted that only the equivalent of the volume of a small drop of water was collected by Cassini. Scientists believe, however, that these few molecules captured could come from hydrothermal reactions between the hot rock and the water beneath the ice crust of the satellite. Enceladus still has many secrets to reveal!
The latest scientific publications describe the presence of abundant water in our solar system and suggest that the Ocean of Enceladus would contain a wide range of CHON essential chemical elements for life (water: H₂O, N: nitrogen, CO₂ : Carbon dioxide, CH₄: methane, etc.). As the measurements made by telescopes like Hubble. The red line to the left of the spectrogram shows the presence of water in huge quantity! The geysers (in blue) at the south pole of the moon and their plumes in the near space are very well visible too. They are no longer clues but evidence now.
This leaves little doubt that this moon could very well according to some researchers have microbial organisms, and even small animals. Imagine the shift for all the mankind.
In terrestrial hydrothermal sources, micro-organisms feed primarily on methane. Is this possible on Enceladus? That is plausible. In an article published last month in the magazine Geophysical Research Letters, a team from the University of Texas at San Antonio had shown the presence of organic gases, such as methane (presence also of H₂, H₂O, NH₃, CO, CO₂ , N₂, HCN, H₂S, etc.) in the atmosphere of Saturn's moon. And this methane would also have originated the geological layers located under the ice of Enceladus. A geological layer conducive to life. A NASA team has also published an interesting statement about these geysers: news.jpl.nasa .gov / Spacecraft Data Suggest Saturn Moon's Ocean May Harbor Hydrothermal Activity.
All the ingredients seem to add up so that a life may have appeared and maintained there as shown by the graph of evolution of the gas populations identified on this moon in order to compare concentrations between Ocean Earth / Ocean Enceladus by Texas researchers, (March 2015).
[cita: We (Texas researchers) first used a mixture of volatiles directly after the INMS (Ion and Neutral Mass Spectrometer) measurements of the plumes (right of the table). The proportion of gas species in the mixture does not allow us to deduce the exact structure of the clathrate (Nda: Block of gas hydrate, ie a compound of organic origin based on methane, with the appearance and consistency of ice, which are gas molecules surrounded by a network of water molecules arranged in a cage, stable under certain conditions of temperature and pressure) (Structure I or Structure II) which could Form in the ocean. Although both CO and CO2 are known to form Clathrate Structure I (Nda: common type of gas hydrate block) [Sloan and Koh, 2008], N2 is inclined to form Structure II structures. Moreover, the ambiguity of the measurements carried out between CO and N2 means that the mixture could also be dominated by the gaseous species forming a structure I or structure II. We therefore show and discuss the results of the study (EN, abstract + pdf) for both cases.]
On Eath, these methane compounds exist and are well known, colloquially called "burning ice" or "methane ice", these ice-cold compounds are flammable as soon as they melt, as in the presence of oxygen or an oxidant. At the molecular level, a methane clathrate is made up of a fine "cage" of ice in which is trapped methane a priori resulting from the decomposition of relatively recent organic matter (compared to that which generated the oil And natural gas) and carried out by anaerobic and methanogenic microorganisms.
De facto, with a chemically active ocean that would have a comparable amount of water to Lake Superior in Canada, and despite the small size of Enceladus with its 500 km, makes it a truly fascinating place to explore.
Recently, the largest moon of Jupiter, Ganymede (Please see the article: Ganymede, an ocean of life?), 5 268 km in diameter, 10 times more than Enceladus, has also been listed as having an ocean under its surface, would place at the same geology-chemical level as Europe and Titan. Like Europe, the ocean of Ganymede would have a depth of about 100 km. Indices suggesting the existence of an immense ocean below the surface had been detected in 2002 by NASA's Galileo probe, but the data was not really conclusive at the time due to the quality of the embedded instruments, notorious for -sized for the mission and not precise enough for the quest for water or life.
Some of the candidates with water or oxygen for the biological part do not pass the formulation Ĕ positively, like the virtual presence of certain ingredients of life for the geo-physico-chemical part and, in fact, would not shelter not life.
Thus on Earth, by this process of geysers, energy is supplied in quantity to the ecosystems found near the hydrothermal sources. Is it the same with Enceladus according to the model admitted below?
On the other hand, it is confirmed that water in large quantities exists on Enceladus both according to the observations and the standard physical calculations as shown by the reference graph of scientists on the various forms of H₂O, below:
However, the project of sending a probe to Enceladus and bringing in various samples, if it were to be validated, will cost about $ 700 million and will take time: it will take 15 to 25 years for the mission To Enceladus alone taking between 5 to 8 years depending on the selected route and the shooting window. So for at best, 2030/2035 to go there and 2040/2045 for the return of samples .... Enceladus is at 1.272 billion km on average of the Earth. It takes 1 h 30 to make a Earth-Enceladus transmission and therefore 3 hours to have an exchange between a local probe and the Earth.
For its part, the European Space Agency (ESA) will send a dedicated probe to study the moons of Jupiter in 2022, the Jupiter Icy Moon Explorer (JIME) which will arrive on site in 2030. This mission will mainly collect data on Ganymede (Please see the article: Ganymede, an ocean of life?), Europe and Callisto, with the avowed aim of seeking clues that could demonstrate whether or not there are extraterrestrial organisms that could thrive in these milieus. The probe is expected to reach Ganymede's orbit around 2033. The global space agencies are not betting on Enceladus to date and indeed no mission to its destination is on the agenda except for projects without precise calendars within NASA.
Discovering living organisms out of the Earth would be one of the most extraordinary scientific events in the history of mankind. Until now, exobiologists have by definition assured that the terrestrial conditions are the most likely to bring together the conditions of life but this seems limiting with the advance of some iconoclastic research against a certain scientific, conceptual and societal orthodoxy. This viewpoint could soon be fully revised and evolved into a more flexible attitude for future extraterrestrial research. More importantly, the philosophical and political significance of such a discovery would be immeasurable. Many religions, politics, and theories about the meaning of life are largely based on the probably unjustified assumption that we are "alone" in this vast universe. The discovery of alien living organisms, even with little intelligence, at the very heart of our own solar system would radically alter the fundamental structures of accepted philosophies and beliefs and confront directly with the teachings of our planetary history and a confronting challenge brutally to the greatest religions of the world. Finally, nothing is done, quite the contrary, to prepare for the future shock of the inevitable discovery of many forms of extraterrestrial lives.
According to the author, the propositional formulation Ĕ thus applied to various celestial bodies within our solar system is a powerful tool that will ultimately make a contribution to the search for life outside the EARTH that is useful enough and its logic will act quickly as A means of overcoming major difficulties in relation to changes in paradigms, mainly because of its mathematical justification as well as the usual and long-standing formulas.
Ultimately, mathematics, often preexisting to a subject of scientific research, always corroborates the observations which they often make in predictors and are always right! Yes Yes.
Finally, three flights of Enceladus by Cassini are scheduled. The next one is scheduled for October 28, 2017, exactly 2 years after the formidable fly-by. To be continued !
DOT.
(CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
Sources: Google, Wikipedia, Research, For Science, arXiv.org, © NASA / JPL / SSI Credits .
[Enceladus, The Life? CNRS-2017. <Hal-01569947> ver1. Id 322178]
Enceladus: Ĕ = 1 - (details), see article "Prospective study of fashion formulation of search for life in the cosmos"
on this blog.
According to the detailed definitions of the factors of the Emergence of life: an inventory of vital conditions quoted on this blog, it appears that Ĕ = 1, and based on this calculation by the formulation Ĕ as the available observations, of life forms populate Enceladus.
 |
| The icy moon of Saturn: Enceladus, 504 km in diameter, seen from Cassini - © NASA / JPL |
According to a part of the scientific community, the study of this moon is likely to allow to discover a form of life or interesting phylogenetics (phylums in french). Since January 2005, announcements and evidences of Life's potential presence have accumulated on Enceladus.
Enceladus has all the requirements for the emergence of life and a peculiarity: its south pole has more than 100 gigantic geysers that expel liquid water into space and with the possibility of life ... The three ingredients of the basic life according to the measurements (heat, water, organic compounds) would therefore be present on Enceladus like other Moons of our Planetary System.
According to the images coming from the Cassini probe, Enceladus is covered with a layer with bluish reflections, characteristic of the snow of fresh water. This "snow" would only be about a hundred meters thick in some places, indicating that it has been snowing on Enceladus for at least 100 million years. The geysers, and the source of underground heat that feeds them, would therefore have been active for a very long time, like several billion years ago.
 |
| Artists' view of creatures |
 |
| Various artist's views of submarine extraterrestrial phylums. |
 |
| Artist's view of seabed on deep ocean moons like Enceladus or Ganymede. |
Meteorite bombardment, which is very ancient throughout the solar system, is also an abundant source of complementary carbon in any medium (eg Antarctic Micrometeorites on Earth) and thus with the carbon intake of these, the theory of the panspermia is not far ...
 | |
| Comets as meteorites have a fundamental role in the quest for life in space |
It is possible that Enceladus was subjected like a Moon to a period of intense bombardment 3.5 to 4 billion years ago without counting the effects of a pounding of the surface even more intense during the Large late bombardment (theoretical period in the history of the solar system approximately 4.1 to 3.9 billion years ago, during which meteoric or cometary impacts would have occurred on the terrestrial planets in a very important way).
Meteorite bombardment is also a source of amino acids, and thus more than 70 amino acids, including 8 of the 20 proteins that are known to be of extra terrestrial origin on Earth since found in many meteorites, for example: Meteorite of Murchison.
In deep space, 141 molecules have been discovered including methane: CH₄, ethyl alcohol: C₂H₅OH, formaldehyde (CH2O) or acetic acid: CH₃COOH as in the Eagle Nebula (M16) and amino acids as on the comet "Tchouri", 67P / Churyumov-Gerasimenko, (ESA, 2004-2016) such as glycine, measured during the CNES Rosetta mission [and also previously detected by the American Stardust probe (NASA, 1999- 2011, and the first to bring particles of a comet back to Earth) in the plume of the Wild 2 comet, as well as phosphorus, an essential component of DNA and many organic compounds have been detected there. Being the sixth comet visited by missions and on which organic compounds are discovered, some mandatory and necessary for life, it seems quite logical to think that the bricks of life are common in the space environment.
 |
| Tchouri_1708 - The comet 67P / Churyumov-Gerasimenko photographed by Rosetta's NavCam camera (© ESA / Rosetta / NavCam) |
Each amino acid consists of an amine function (NH 2), a carboxylic acid function (COOH-) and a variable side chain (R).
 |
| Structure of an amino acid, CHON. Wikipedia, cc by its 3.0 |
Amino acids are molecules that are part of the protein composition and vital for the proper functioning of any living metabolism. These bonds are called peptides. There are about 100 amino acids, but only 22 are coded by the genome of living organisms, 4 of which are DNA. Each amino acid gives the protein specific chemical properties, and the assembly order gives it a very precise 2D and 3D function and can be folded back.
From an exobiological point of view, essential and varied ion exchanges are therefore at stake between rock and liquid water, in keeping with the existence of possible forms of life according to our knowledge. It is still unclear whether there are all the necessary components but to date, many are available and can be reunited so that life exists on Enceladus. In any case, there are many reactions of oxydo-reductions and redox in action there! This satellite is one of only four objects in the Solar System (with Jupiter's satellite, Io, Neptune's, Triton's, and of course the Earth's) on which eruptions or material ejections could be directly observed.
Enceladus revolves around Saturn (Saturn has 62 known moons, 53 of which have formal names; in addition, there is evidence of dozens to hundreds of moonlets with diameters of 40–500 meters in Saturn's rings, which are not considered to be true moons) within the outermost and most tenuous ring of all, called ring E; this ring would be fed permanently in particles by the current (or recent) "volcanic eruptions" of Enceladus that one could also go to study. Moreover, the formidable tidal forces as plasma fluxes resulting from the gravitational action of the neighboring giant Saturn form an enormous energy supply, and a geophysical argument favourable to the hypothesis of the presence of life in the form of creatures diverse and perhaps not so strange on this moon as others around some solar planets and subsequently in other stellar and exolune systems ...
 |
| Enceladus_Atmosphere_(Artist's_Concept)_PIA06430.jpg - public domain |
It is therefore necessary also to analyse its neighbours within the ring E, namely three major internals satellites of Saturn which orbit there, in the company of the three small moons of the group of Alcyonides, namely:
- Mimas, with a diameter of 396 km, which is the smallest of the four (including Enceladus). It is ovoid in shape, slightly flattened at the poles and swollen at the level of the equator. The front of Mimas is marked by a large crater of 130 kilometers in diameter, called Herschel crater. Its surface is dominated by the presence of craters of impacts, and shows no trace of geological activity.
- Tethys, with 1,066 km in diameter, is the 5th largest moon of Saturn (and the second of the internal moons). Its surface is characterized by the presence of a gigantic fault, Ithaca Chasma, which bar part of its surface, and of the Odyssée crater, with a diameter of 400 km. Ithaca Chasma is almost concentric with the Odyssey crater, and these two geological formations could be linked.Tethys has no visible geological activity. The majority of its surface is strongly cratered, and the hemisphere opposite Odyssey has a younger surface. The density of Tethys (0.97 g / cm3) is lower than that of water, indicating that the moon is predominantly ice, with a low proportion of rocks.
- Dione, which is very similar to Rhea, with its 1,123 km diameter, is the fourth largest satellite of Saturn and the largest of the internal moons. The majority of its surface is covered with impact craters but shows filaments corresponding to ice cliffs a few hundred meters high, indicating past or persistent geological activity. Cassini's measurements also show that Dioné is a source of plasma in Saturn's magnetosphere, indicating that it could still be geologically active on a scale probably less important than Enceladus. And also has an ocean of sub-surface hidding a global ocean beneath its icy crust! Thus the ocean of Dione probably exists since the birth of the star and will constitute a stable zone for a long time with a possible habitability conducive to the development of Life has a minimum of microbial stage .... Especially since it is also in direct contact with the rocks of the nucleus like Enceladus or Ganymede (see the articles on this blog), and "rocks-water interactions offer both essential nutrients and energy, two vital ingredients for life", underlines Attilio Rivoldini, one of the authors of the study published in the Geophysical Research Letters.
Note: It may be speculative to date to use the model Ĕ but it is a tool that can be useful now and will soon be validated by the various data collected.
Since 2012, NASA has been conducting missions such as LIFE (Life Investigation For Enceladus, pdf of description of the mission) by Peter TSOU, or the Enceladus Life Finder mission that was proposed in 2015 to finance the Discovery Mission Mission, one of NASA's exploration programs.
The final design of Life Investigation For Enceladus (LIFE) in 2015 includes a sample return module inherited from the Japanese Haybusa probe (ie: Peregrine Falcon, which reached asteroid Itokawa in 2005, the capsule containing the samples is returned at a short distance from the Earth on June 13, 2010. This capsule, in the shape of a saucer, measured 40 cm in diameter and 25 cm in height for a mass of approximately 17 kg. The end facing forward during atmospheric reentry was covered by an ablative heat shield 3 cm thick to protect its contents from heat, close to 3000 ° C, generated
 by its re-entry speed, and the receptacle contained 1543 particles, the size of which was between 3 and 40 micrometers) and equipped with a multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG for Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator)
by its re-entry speed, and the receptacle contained 1543 particles, the size of which was between 3 and 40 micrometers) and equipped with a multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG for Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator)If one of them is selected, a preparation date for the launch to 31 December 2021 may still be possible. The project is to collect water / particles ejected in space with a probe equipped with a battery of collectors and instruments of measurements of analysis in situ, in space, to verify the nature of the elements The speed of release at the surface of Enceladus is about 865 km / h, ie 0.241 km / s, which is not too much of a problem, but probing the very deep, is out of our present means, and this with a mission of study even more important because a priori, science has no direct evidence of the reality of a local life. However, as a more precise and thorough analysis of the compounds released from these hydrothermal sources is necessary, it will be necessary at all costs to bring the recovered samples back to Earth. The probe would have only to position itself at the South pole to collect water samples in space, and thanks to its built-in instruments try to measure, classify, inventory, record all particles and informations for the search for Life on Enceladus and then return to Earth so that scientists can better study direct evidence harvested ....
 |
| Southern Pole of Enceladus seen from Cassini - © NASA / JPL |
The raw images of the water geysers and the Enceladus flyover are here: https://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?feature=4759
Compared to the Earth, micro-organisms in the hydrothermal springs of the famous Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming derive most of their energy from hydrogen, not sulfur, as was thought. Research conducted over several years led a team from the University of Colorado to Boulder to this conclusion. The researchers first studied the phylogenetic composition of microbial populations living in hot springs in Yellowstone at over 70 ° C. Molecular analyzes have shown that the majority of the biomass of these systems is composed of organisms using hydrogen oxidation to obtain energy.
Finally, computer-generated thermodynamic (energy study) models have completed a portrait of an extremophilic ecosystem based on hydrogen-related metabolic functioning despite high sulfur content.
The NASA has already announced the discovery of many types of molecules including hydrogen on Enceladus on its surface, thanks to a brief overview of the Cassini probe (launched in 2004) which was carried out at an altitude of 49 kilometers at the SOUTH pole, October 28, 2015, through plumes of water vapor and ice particles, which could be an indication of the presence of extraterrestrial life in the Solar System. It is the instrument Ion and Neutral Mass Spectrometer (INMS) embarked that analyzed the composition, this one was originally intended to study the upper layers of the atmosphere of Titan.
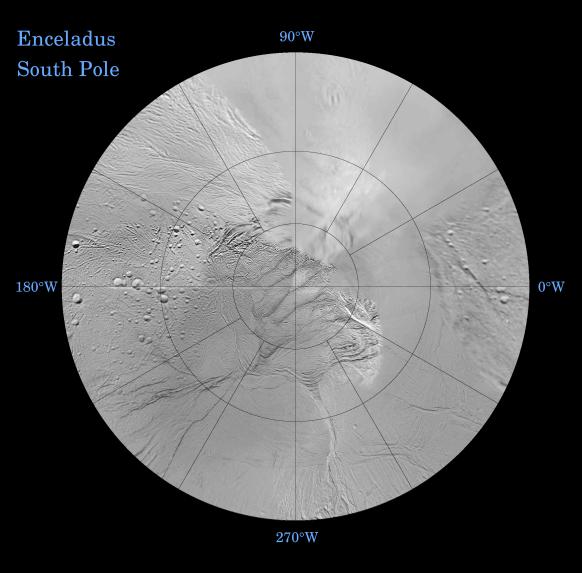 |
| South Pole of Enceladus - © NASA / JPL |
It should be noted that only the equivalent of the volume of a small drop of water was collected by Cassini. Scientists believe, however, that these few molecules captured could come from hydrothermal reactions between the hot rock and the water beneath the ice crust of the satellite. Enceladus still has many secrets to reveal!
The latest scientific publications describe the presence of abundant water in our solar system and suggest that the Ocean of Enceladus would contain a wide range of CHON essential chemical elements for life (water: H₂O, N: nitrogen, CO₂ : Carbon dioxide, CH₄: methane, etc.). As the measurements made by telescopes like Hubble. The red line to the left of the spectrogram shows the presence of water in huge quantity! The geysers (in blue) at the south pole of the moon and their plumes in the near space are very well visible too. They are no longer clues but evidence now.
 |
| Credits : NASA-GSFC/SVS, Hubble Space Telescope, Stefanie Milam, Geronimo Villanueva |
This leaves little doubt that this moon could very well according to some researchers have microbial organisms, and even small animals. Imagine the shift for all the mankind.
 |
| The geysers on the ocean floor form the heart of extremely rich ecosystems of life. They were discovered in the spring of 1977 at a depth of 2600 meters at the intersection of tectonics plates. |
In terrestrial hydrothermal sources, micro-organisms feed primarily on methane. Is this possible on Enceladus? That is plausible. In an article published last month in the magazine Geophysical Research Letters, a team from the University of Texas at San Antonio had shown the presence of organic gases, such as methane (presence also of H₂, H₂O, NH₃, CO, CO₂ , N₂, HCN, H₂S, etc.) in the atmosphere of Saturn's moon. And this methane would also have originated the geological layers located under the ice of Enceladus. A geological layer conducive to life. A NASA team has also published an interesting statement about these geysers: news.jpl.nasa .gov / Spacecraft Data Suggest Saturn Moon's Ocean May Harbor Hydrothermal Activity.
All the ingredients seem to add up so that a life may have appeared and maintained there as shown by the graph of evolution of the gas populations identified on this moon in order to compare concentrations between Ocean Earth / Ocean Enceladus by Texas researchers, (March 2015).
[cita: We (Texas researchers) first used a mixture of volatiles directly after the INMS (Ion and Neutral Mass Spectrometer) measurements of the plumes (right of the table). The proportion of gas species in the mixture does not allow us to deduce the exact structure of the clathrate (Nda: Block of gas hydrate, ie a compound of organic origin based on methane, with the appearance and consistency of ice, which are gas molecules surrounded by a network of water molecules arranged in a cage, stable under certain conditions of temperature and pressure) (Structure I or Structure II) which could Form in the ocean. Although both CO and CO2 are known to form Clathrate Structure I (Nda: common type of gas hydrate block) [Sloan and Koh, 2008], N2 is inclined to form Structure II structures. Moreover, the ambiguity of the measurements carried out between CO and N2 means that the mixture could also be dominated by the gaseous species forming a structure I or structure II. We therefore show and discuss the results of the study (EN, abstract + pdf) for both cases.]
On Eath, these methane compounds exist and are well known, colloquially called "burning ice" or "methane ice", these ice-cold compounds are flammable as soon as they melt, as in the presence of oxygen or an oxidant. At the molecular level, a methane clathrate is made up of a fine "cage" of ice in which is trapped methane a priori resulting from the decomposition of relatively recent organic matter (compared to that which generated the oil And natural gas) and carried out by anaerobic and methanogenic microorganisms.
De facto, with a chemically active ocean that would have a comparable amount of water to Lake Superior in Canada, and despite the small size of Enceladus with its 500 km, makes it a truly fascinating place to explore.
Recently, the largest moon of Jupiter, Ganymede (Please see the article: Ganymede, an ocean of life?), 5 268 km in diameter, 10 times more than Enceladus, has also been listed as having an ocean under its surface, would place at the same geology-chemical level as Europe and Titan. Like Europe, the ocean of Ganymede would have a depth of about 100 km. Indices suggesting the existence of an immense ocean below the surface had been detected in 2002 by NASA's Galileo probe, but the data was not really conclusive at the time due to the quality of the embedded instruments, notorious for -sized for the mission and not precise enough for the quest for water or life.
Some of the candidates with water or oxygen for the biological part do not pass the formulation Ĕ positively, like the virtual presence of certain ingredients of life for the geo-physico-chemical part and, in fact, would not shelter not life.
 |
| Enceladus section with a 30-40 km thick ice sheet with an ocean of about 10 km depth and a hundred geysers observed at the South Pole. © Credits Nasa, JPL-Caltech |
Thus on Earth, by this process of geysers, energy is supplied in quantity to the ecosystems found near the hydrothermal sources. Is it the same with Enceladus according to the model admitted below?
 |
ENCELADUS 'COLD GEYSER'
© Nasa, JPL, SSI Credits |
On the other hand, it is confirmed that water in large quantities exists on Enceladus both according to the observations and the standard physical calculations as shown by the reference graph of scientists on the various forms of H₂O, below:
 |
| Summary diagram of the known H₂O states (depending on temperature and pressure). by CMG Lee cc-by-sa-20 Credits |
However, the project of sending a probe to Enceladus and bringing in various samples, if it were to be validated, will cost about $ 700 million and will take time: it will take 15 to 25 years for the mission To Enceladus alone taking between 5 to 8 years depending on the selected route and the shooting window. So for at best, 2030/2035 to go there and 2040/2045 for the return of samples .... Enceladus is at 1.272 billion km on average of the Earth. It takes 1 h 30 to make a Earth-Enceladus transmission and therefore 3 hours to have an exchange between a local probe and the Earth.
For its part, the European Space Agency (ESA) will send a dedicated probe to study the moons of Jupiter in 2022, the Jupiter Icy Moon Explorer (JIME) which will arrive on site in 2030. This mission will mainly collect data on Ganymede (Please see the article: Ganymede, an ocean of life?), Europe and Callisto, with the avowed aim of seeking clues that could demonstrate whether or not there are extraterrestrial organisms that could thrive in these milieus. The probe is expected to reach Ganymede's orbit around 2033. The global space agencies are not betting on Enceladus to date and indeed no mission to its destination is on the agenda except for projects without precise calendars within NASA.
 |
| Jupiter Icy Moon Explorer or spaceship Prometheus 1 - PD-USGov-NASA Credits |
Discovering living organisms out of the Earth would be one of the most extraordinary scientific events in the history of mankind. Until now, exobiologists have by definition assured that the terrestrial conditions are the most likely to bring together the conditions of life but this seems limiting with the advance of some iconoclastic research against a certain scientific, conceptual and societal orthodoxy. This viewpoint could soon be fully revised and evolved into a more flexible attitude for future extraterrestrial research. More importantly, the philosophical and political significance of such a discovery would be immeasurable. Many religions, politics, and theories about the meaning of life are largely based on the probably unjustified assumption that we are "alone" in this vast universe. The discovery of alien living organisms, even with little intelligence, at the very heart of our own solar system would radically alter the fundamental structures of accepted philosophies and beliefs and confront directly with the teachings of our planetary history and a confronting challenge brutally to the greatest religions of the world. Finally, nothing is done, quite the contrary, to prepare for the future shock of the inevitable discovery of many forms of extraterrestrial lives.
According to the author, the propositional formulation Ĕ thus applied to various celestial bodies within our solar system is a powerful tool that will ultimately make a contribution to the search for life outside the EARTH that is useful enough and its logic will act quickly as A means of overcoming major difficulties in relation to changes in paradigms, mainly because of its mathematical justification as well as the usual and long-standing formulas.
Ultimately, mathematics, often preexisting to a subject of scientific research, always corroborates the observations which they often make in predictors and are always right! Yes Yes.
Finally, three flights of Enceladus by Cassini are scheduled. The next one is scheduled for October 28, 2017, exactly 2 years after the formidable fly-by. To be continued !
DOT.
(CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
Sources: Google, Wikipedia, Research, For Science, arXiv.org, © NASA / JPL / SSI Credits .








Commentaires
Enregistrer un commentaire